CELERO a free of charge web-based open source software platform, which merges Cleaner Production (CP) and Industrial Symbiosis (IS).
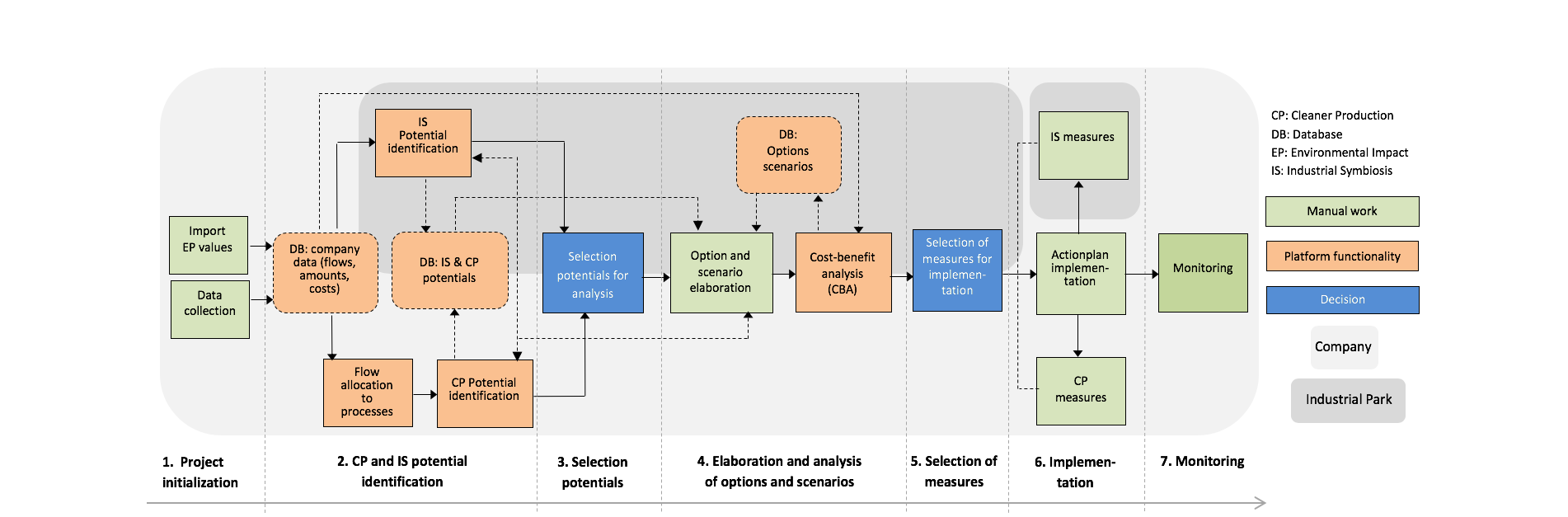
The work flow for CELERO users to improve the eco-efficiency of industrial processes is based on a combined CP and IS approach consists of the following seven steps 1) Project initialisation, 2) CP and IS potential identification, 3) Selection of promising potentials for further analysis, 4) Option and scenarios elaboration with Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA), 5) Selection of measures for implementation, and 6) Implementation and sharing success stories. These steps and the functionalities of CELERO to support the user to improve eco-efficiency are explained below.
1. Project initialisation: To start a new project a user creates a resource efficiency project with the help of the project management functionality. With the provided dataset management, the user enters flow data (amounts, costs and characteristics), products and processes data of the companies into the system. For the calculation of the environmental impact each user need to import and maintain specific environmental impacts values (e.g kPt UBP/kg material) value.
2. CP and IS potential identification:
a. For CP potential identification, shares of the total amounts of material flows (stored in the database) are allocated manually to the identified and defined production processes. Only flows and processes that are identified to be relevant for the environment or the costs should be considered. The allocation is made manually and the user needs expert knowledge of the investigated processes. If detailed information on process level is lacking, as often the case, experts need to make rough estimates based on site visits and judgements to allow an overview and initiate further investigations if deemed necessary for robust decisions. A first graphical visualisation of the findings provides the experts with a useful overview of the environmental impact and the costs of processes that already allow a first clustering of CP potentials. For enhanced scoping the system supports the calculation of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and a comparison against benchmarks. The user selects or defines the KPIs in the tool and enters benchmark values including a short description. Benchmarks can be found either in the section case studies of CELERO or must be searched in literature. The KPI benchmark comparison is displayed in a bar chart and supports the selection of CP potentials for further analysis. The user should select these processes and flows for option generation and should start with the processes that show the most negative deviation from KPIs against benchmarks. If a best practice for a process was chosen as a benchmark the best practice already represents an improvement option.
b. For IS potential identification matches between products, by-products, wastes, services and infrastructures among industries can be searched automatically or manually. Users can select material and energy flows among a list of categories and select companies to be investigated for potential matches. A list of potential symbiosis is generated based on a flow names (character chains) comparison. If a specific flow has been entered with different names for different companies, users can manually create a match between these characteristically equal flows with different names. IS potentials can be saved, modified if more precise data are collected and then recalled in the cost benefit analysis module for further analysis. Integrated maps also allow users to spatially analysis a match and calculate transport distances between companies.
3. Selection of promising potentials for further analysis: The initial CP & IS potential identification leads to a first phase of decision-making where potentials are selected for further investigation. At this stage the decision making entity respectively industrial park/regional managers should be involved. In parallel, immediately after initial data collection, the potential options of "low hanging fruits" can be identified and should be implemented directly avoiding any intermediate steps.
4. Option and scenarios elaboration with Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA): The elaboration of CP and IS options and scenarios is creative work of the experts. For the CBA a user needs to provide all flow and process data, e.g. amounts, costs environmental impact etc., except the data already collected and calculated for the KPI benchmark comparison. By comparing the environmental and economic values of the base line with the options and scenarios, the system calculates the parameters of a cost-benefit curve and displays it. Options and scenarios which have the highest environmental benefit and lowest specific costs, preferably savings, for the reduction of the environmental impact (marginal costs/savings) are candidates for implementation.
5. Selection of measures for implementation: The results of the CBA support the decision on which options and scenarios shall be implemented as measures, but additional decision criteria of the company have to be taken into consideration as well, e.g. investment cycle, production plans, capacity for implementation and operation of options, payback time or initial investment costs etc. Decisions on different level can be supported, i.e. whether measures shall be implemented to improve the eco-efficiency of a single company with CP measures or a network of industries with IS measures or a combination. This depends on objectives of the involved stakeholders and their level of cooperation. The selection of the most promising measures also in this case depends on other criteria as mentioned above.
6. Implementation and sharing success stories: The implementation of measures happens outside of CELERO in the real world. However success stories and best practices should be shared with the CELERO user community. Therefore a user should elaborate a best practice fact sheet after implementation and provide it for storing it in the section case studies.